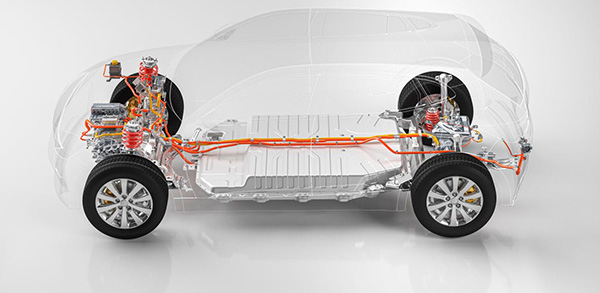
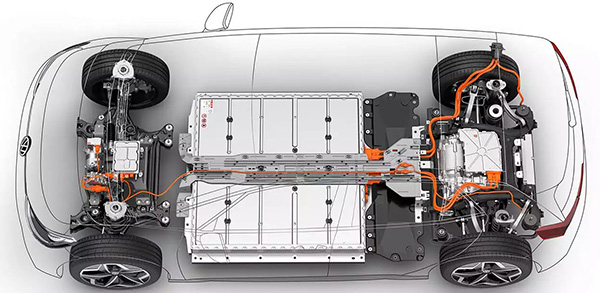
Potential Safety Hazards of Electric Vehicles
Potential safety hazards of battery electric vehicles include high-voltage electric shock, power battery leakage & combustion, and other risks that may exist in vehicles under special circumstances.

In recent years, lithium-ion batteries have been widely used in pure electric and hybrid vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries will not have safety problems during normal use, but the abuse of batteries will aggravate the thermal effect of batteries, manifested as "thermal runaway", thus cause safety problems. The following conditions can lead to thermal runaway:
(1) Overcharge and overdischarge;
(2) Overcurrent;
(3) Overheated battery.
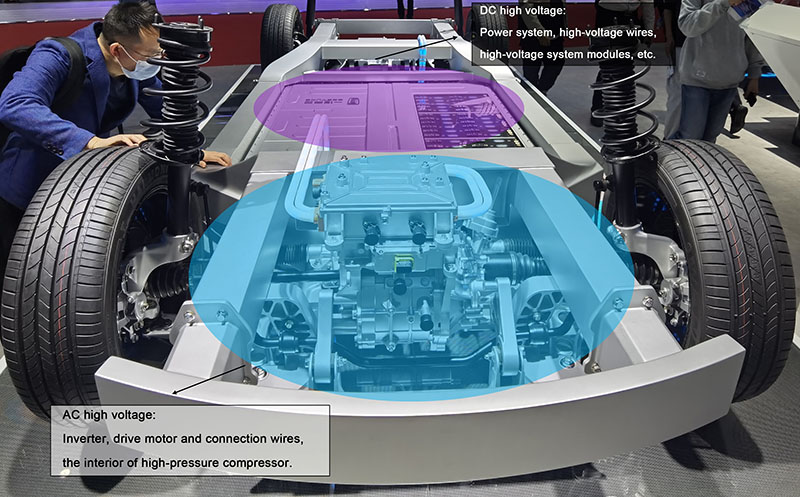
AC high voltage: It is mainly distributed between the inverter and the electric motor, as well as between the charging socket and the on-board charger (OBC). The difference is that the former is usually around 300V, while the latter is the 220V/380V voltage of the external power grid.
DC high voltage: It is mainly distributed between the battery pack and various driving components. For example, the connection between the power battery and the drive inverter is a DC high voltage; so as the connection between the battery and the high-voltage compressor.
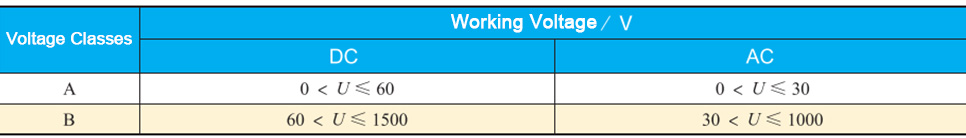
The battery pack in an electric vehicle is built with hundreds of small cells that store electrical energy. The cells are connected together in series so that their combined voltage adds up to 300V-600V, or even higher. According to the electrically propelled road vehicles safety specifications GB/T 18384.3-2015, the maximum allowable voltage for human contact is less than 60V DC/30V AC. However, the power battery of a pure electric vehicle has a voltage that exceeds 600V, which is far exceeded the limit that the human body can bear.
Current: The current can be divided into two categories: low-voltage current and high-voltage current. The former is generally less than 100V, while the latter can be 300V or more. If the human body touches electricity at home or at work, it will usually receive low-voltage current and only feel uncomfortable. However, if you touch high-voltage current such as those found in EVs, it will cause serious injury or even death.
The high-voltage electrical components are shown in the figure:

If the high-voltage components are damaged or wet inside, it is possible to transfer a potential to the housing. Dangerous voltages can arise when different potentials develop between the housings of two high-voltage components. At this time, if the operator touches these components, there is a risk of electric shock. The threshold value of the leakage current that is safe for the human body is 2mA. That is to say, when a person directly touches any point of the electrical system, the current flowing through the human body should be less than 2mA, and then the vehicle insulation is considered qualified.
1. Power Battery Safety
Electric vehicles (EVs) use rechargeable batteries that can be recharged from the electric grid or from regenerative braking. The power battery is a significant safety concern because of its size, weight, and power requirements. In addition to potential fires, the batteries may overheat and cause injuries if they are not properly cooled or ventilated. If the battery catches fire, there is a possibility that it will explode and cause injury to persons nearby or damage to property within range of the blast.
(1) Overcharge and overdischarge;
(2) Overcurrent;
(3) Overheated battery.
2. Safety in Hazardous Operating Conditions
The safety concerns regarding electric vehicles are similar to those of regular vehicles. However, due to the high voltage and energy density of lithium-ion batteries, there are additional hazards that must be addressed. EVs are not suitable for use in extreme weather conditions such as heavy snow or rain. if submerged, they could short circuit and cause damage to the vehicle. In addition, if the vehicle goes through unexpected movement while charging, then it may cause damage to vehicle body components or even cause serious safety issues.3. Electrical Safety
The electrical safety of electric vehicles mainly includes the protection against electric shock to the personnel, reasonable distribution of battery energy, high voltage safety during charging, driving and maintenance, and electrical safety in case of collision.
DC high voltage: It is mainly distributed between the battery pack and various driving components. For example, the connection between the power battery and the drive inverter is a DC high voltage; so as the connection between the battery and the high-voltage compressor.
The battery pack in an electric vehicle is built with hundreds of small cells that store electrical energy. The cells are connected together in series so that their combined voltage adds up to 300V-600V, or even higher. According to the electrically propelled road vehicles safety specifications GB/T 18384.3-2015, the maximum allowable voltage for human contact is less than 60V DC/30V AC. However, the power battery of a pure electric vehicle has a voltage that exceeds 600V, which is far exceeded the limit that the human body can bear.

The high-voltage electrical components are shown in the figure:

Message
If you are interested in our products, please fill in the message form below. Our sales representative will contact you within 24 hours.