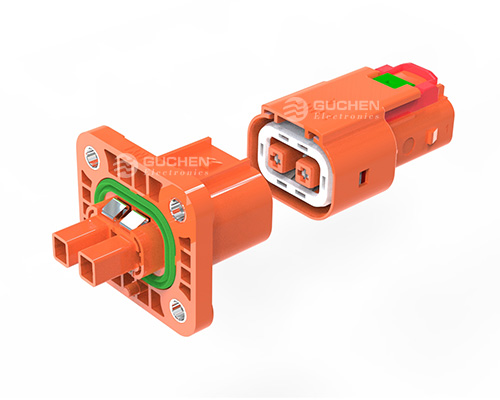
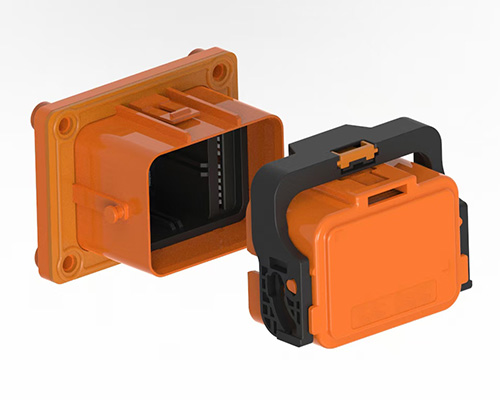
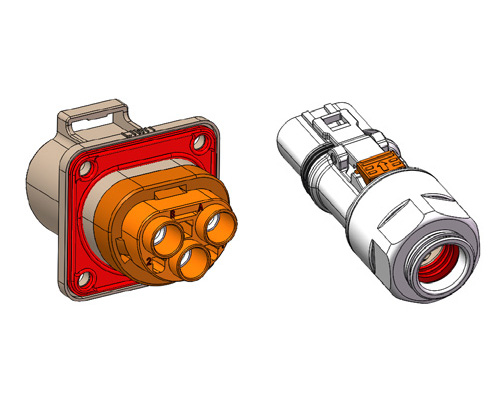
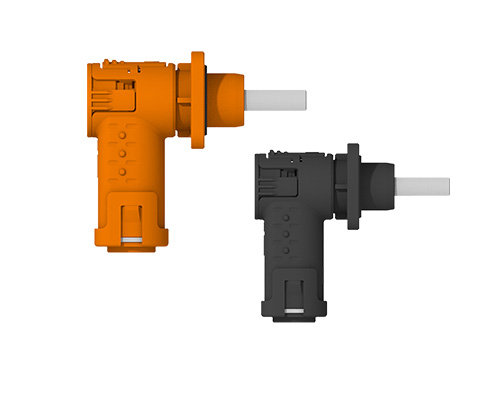
Revealing the MSD Service Disconnect: A Key to Electrical Safety!
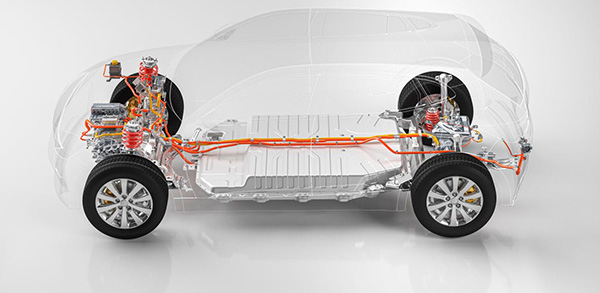
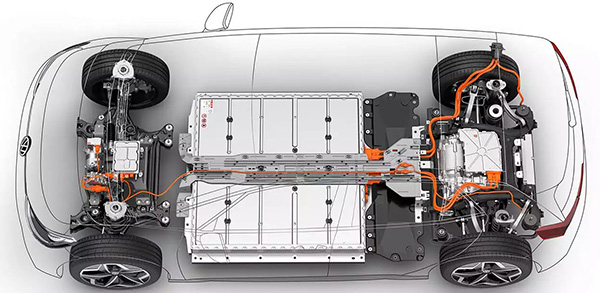
The MSD (Manual Service Disconnect), as an advanced high-voltage fuse solution, is widely used in the field of new energy technologies. Its primary function is to provide comprehensive protection for high-voltage systems such as electric vehicles, charging stations, and wind and solar power equipment. During system maintenance or servicing, the MSD ensures a safe and reliable working environment, effectively protecting technicians and preventing unexpected system damage caused by short circuits or overloads.
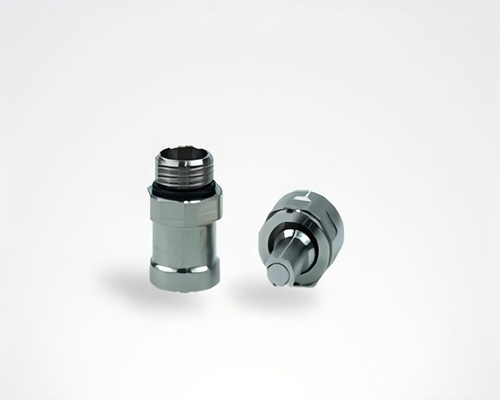
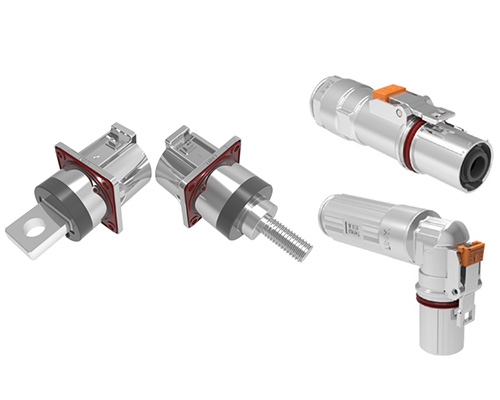
At Shenzhen Guchen Electronic, our MINI MSD series is rated for 80A to 400A fuse currents, offering excellent protection for mid- to high-power systems in compact spaces.
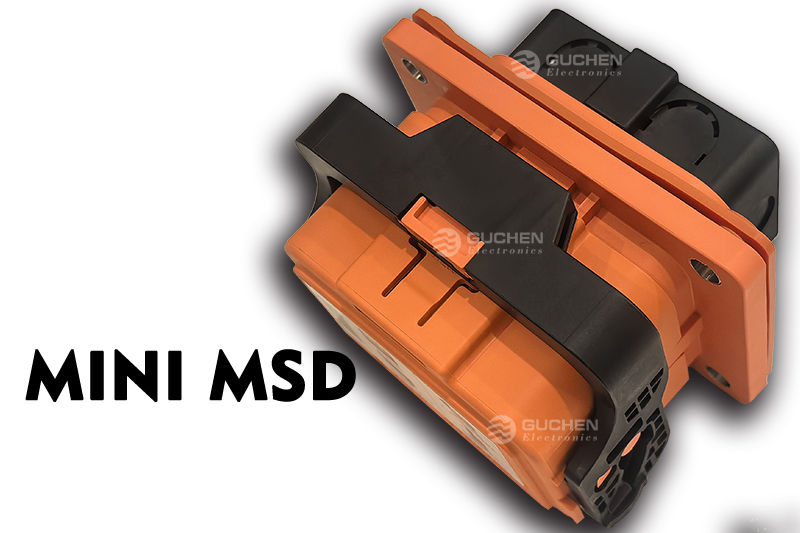

When an external short circuit is detected, the built-in fuse will quickly disconnect the high-voltage circuit, preventing equipment damage or safety incidents caused by excessive current. When manual disconnection is required for maintenance or other operations, the system will first trigger the HVIL function, then disconnect the high-voltage circuit to ensure operational safety.
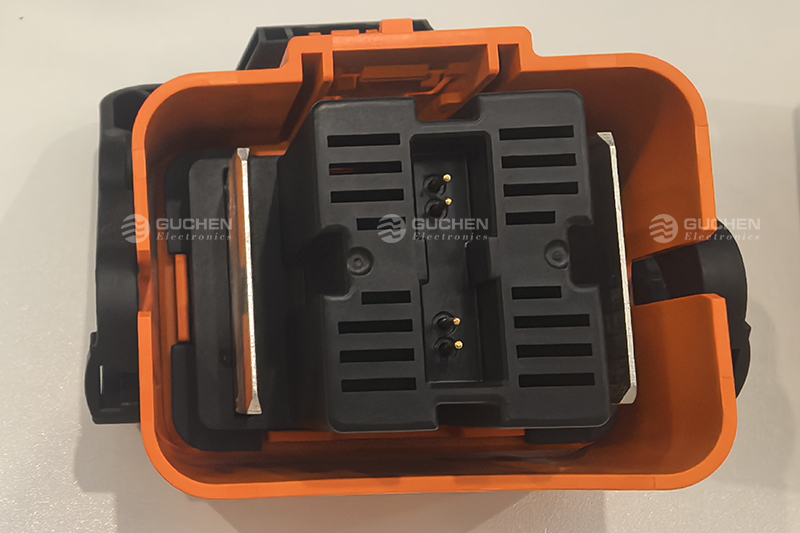

MSDs must also meet key performance requirements including temperature adaptability, overload protection, chemical corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Environmental stress resistance and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) should also be considered to ensure long-term safety and stability.
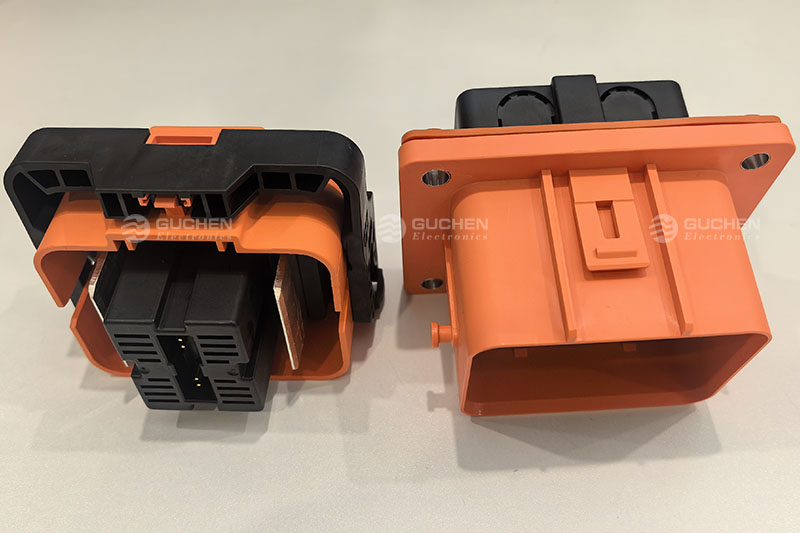

The locking function of the MSD effectively prevents operational errors. This design significantly reduces the risk of equipment failure caused by incorrect operations and greatly minimizes potential safety accidents.
◆ Enhances Operational Safety
Strengthening the MSD's locking mechanism can significantly improve overall system safety, helping to prevent injuries and property damage caused by equipment faults.
◆ Extends Service Life
Optimizing the MSD locking structure can effectively prolong product lifespan, reducing the cost of maintenance and replacement.
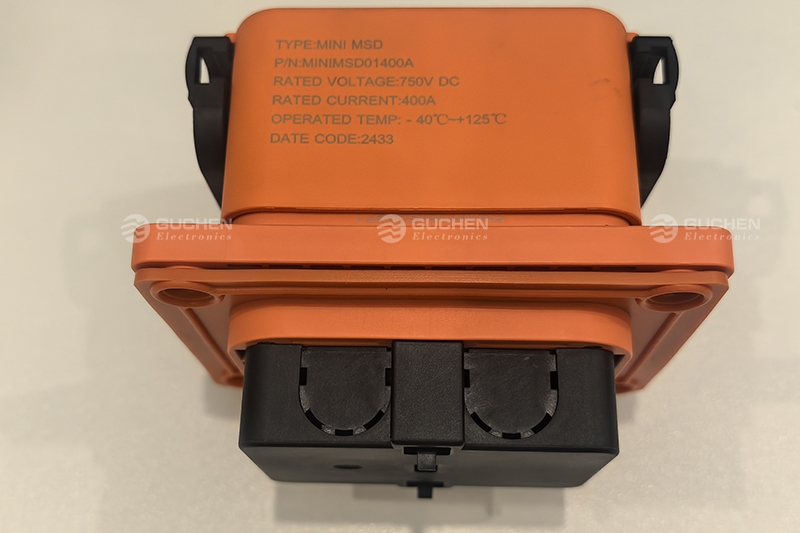

At Shenzhen Guchen Electronic, our MINI MSD series is rated for 80A to 400A fuse currents, offering excellent protection for mid- to high-power systems in compact spaces.

01 What is MSD?
MSD stands for Manual Service Disconnect, designed specifically for the high-voltage circuits of electric vehicles to provide protection during maintenance and emergency scenarios. This device is typically integrated into the main circuit of the battery pack and equipped with a high-voltage fuse and HVIL (High Voltage Interlock) function.When an external short circuit is detected, the built-in fuse will quickly disconnect the high-voltage circuit, preventing equipment damage or safety incidents caused by excessive current. When manual disconnection is required for maintenance or other operations, the system will first trigger the HVIL function, then disconnect the high-voltage circuit to ensure operational safety.

02 Key Functions an MSD Must Have
1) Flame Resistance Compliance
Except for the fuse, all other materials in the MSD must be plastic and must comply with UL94 V-0 flammability rating standards. According to the latest national standards, the burn test duration must reach 130 seconds. If the MSD lacks sufficient flame resistance, external flames could penetrate into the battery pack through the MSD, posing an unacceptable safety risk.2) IP Rating Compliance
MSDs are typically installed on the battery pack’s top cover. To ensure the pack meets IP67 or IP6K9K protection standards, the MSD must also meet these same IP rating requirements. Therefore, when selecting an MSD, these should be considered as basic parameters, and suppliers should be required to provide verification reports to demonstrate compliance. If conditions permit, it is recommended to conduct vibration tests before performing IP67 or IP6K9K tests to ensure the component can maintain its protection level throughout the entire service life of the pack.3) IP Protection Compliance in All States
When connected, the MSD must comply with IPXXD standards, and when disconnected, it must meet IPXXB standards. This requirement is often overlooked, but is critical—failure to meet IPXXB means that human fingers may come into contact with high-voltage components, which is strictly prohibited.4) Tool-Free Manual Disconnection
The MSD must allow for manual disconnection without any tools. This manual operation must be highly repeatable and be capable of at least 50 connection/disconnection cycles. However, actual usage demands may far exceed this number, with expectations reaching 500 cycles or more.MSDs must also meet key performance requirements including temperature adaptability, overload protection, chemical corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Environmental stress resistance and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) should also be considered to ensure long-term safety and stability.

03 Locking Structure Function of MSD
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an MSD
- Rated Voltage: If the battery pack's maximum voltage approaches 400V, select an MSD with a rated voltage of at least DC450V.
- Continuous Load Current: The rated current of the MSD should be at least twice the system’s continuous current to ensure stable operation.
- Peak Load Current: The MSD’s peak current capability must exceed the actual system peak load to ensure system stability.
- Response Time: The MSD's disconnection response time must be shorter than the time it takes for relay sticking faults to occur.
Functions of the MSD Locking Structure
◆ Prevents MisoperationThe locking function of the MSD effectively prevents operational errors. This design significantly reduces the risk of equipment failure caused by incorrect operations and greatly minimizes potential safety accidents.
◆ Enhances Operational Safety
Strengthening the MSD's locking mechanism can significantly improve overall system safety, helping to prevent injuries and property damage caused by equipment faults.
◆ Extends Service Life
Optimizing the MSD locking structure can effectively prolong product lifespan, reducing the cost of maintenance and replacement.

04 MSD Maintenance
The MSD, as a critical component of the vehicle’s electrical system, consists of two main parts: the plug connector and the receptacle. The receptacle is typically fixed to the battery pack enclosure or the high-voltage distribution box, while the plug can be configured with a fuse or directly connected using copper busbars. Notably, MSDs equipped with fuses also provide short-circuit protection, further enhancing system safety.◆ Visual Inspection of MSD
Check the overall appearance of the MSD to ensure there are no signs of damage, deformation, or impact. This includes careful observation to confirm the external casing is intact and undamaged.◆ Plug Connector Inspection
Inspect all components such as waterproof seals, terminals, fuses, locking clips, and locking pins. Look for signs of damage, deformation, impact marks, or discoloration to ensure full functionality.◆ Fuse Inspection
To ensure normal function and secure installation of the fuse, use a digital multimeter to measure the resistance value. This verifies whether the fuse is operating within the specified working range, thus ensuring the electrical safety and stability of the system.◆ HVIL Testing
The HVIL testing of the MSD plug connector aims to ensure the reliability of the connection and prevent vehicle faults caused by electrical issues. This includes:- Measuring connection stability with a multimeter
- Performing insulation tests with an insulation tester to detect any potential faults and ensure vehicle safety
◆ Receptacle Reliability Check
Comprehensively inspect the receptacle for any signs of looseness, breakage, corrosion, and check for proper sealing. Use a digital multimeter to verify reliable electrical connection, ensure the mechanical fasteners are secure with appropriate tools, and conduct insulation resistance testing using an insulation tester to confirm electrical safety.
Message
If you are interested in our products, please fill in the message form below. Our sales representative will contact you within 24 hours.